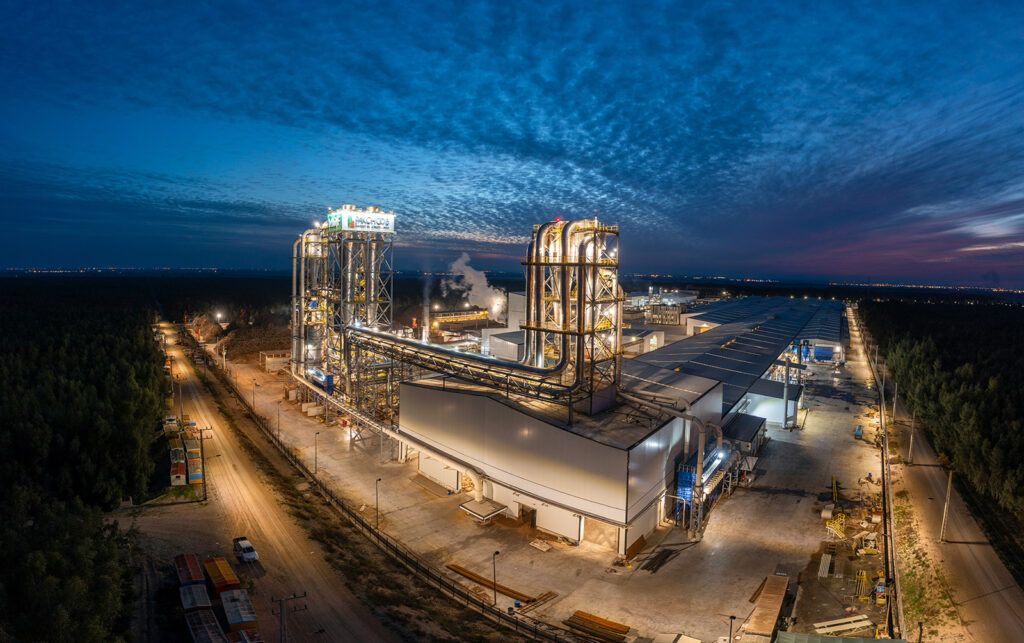
Smart Energy-Saving Trends: An In-Depth Look at Dimmable Industrial & Outdoor LED Lighting and the ODM Partnership Model
I. A New Era in Lighting: The Integration of Intelligence and Energy Efficiency
The global lighting market is shifting from simply “providing light” to “providing light intelligently,” making dimming capabilities a standard requirement for industrial, commercial, and outdoor lighting. Businesses face core challenges in high-intensity lighting scenarios (like factories, streets, and large malls): achieving significant energy savings, improving lighting comfort, and reducing maintenance costs. The solution lies in Dimmable LED technology, and choosing a technically proficient ODM manufacturer is key to its successful implementation.
II. Key Technology Deep Dive: Why “Dimmable” is Core to High-End Lighting
Introduction to Dimming Technology Principles:
Mainstream dimming protocols primarily include:0-10V Dimming: A simple, stable, low-cost analog protocol using a 0-10V voltage signal to control brightness. Valued for its reliability and ease of maintenance, it’s widely used in industrial settings like factories and warehouses with high-bay lights, where stable group control suffices and individual lamp control is not critical.
DALI Dimming: A digital protocol supporting two-way communication. Each luminaire has a unique address, enabling precise individual control, status monitoring, and scene setting. This makes it a favorite for smart city streetlights, meeting needs for remote monitoring, fault alarms, and on-demand lighting.
Wireless Dimming (Zigbee/Bluetooth): Controlled via wireless signals, eliminating the need for separate control wiring and offering flexible installation. Ideal for smart homes, retrofit projects, and as a supplement to smart streetlight systems, facilitating integration into IoT platforms.
PWM Dimming: A fundamental technique achieving excellent dimming by rapidly switching the current, typically built into the LED driver, ensuring high-quality, flicker-free performance.
In summary, the choice depends on the application: industrial settings prioritizing stability and cost often use 0-10V, while scenarios like smart cities requiring granular management prefer DALI or wireless technologies.
Core Value of Dimmable Lighting:
Maximum Energy Savings: Enables “lighting on demand,” drastically reducing waste from over-lighting and lowering electricity costs.
Extended Lifespan: Reduces operating current and temperature, significantly prolonging luminaire life.
Enhanced Comfort & Flexibility: Allows seamless brightness adjustment based on time, scenario, or activity, improving the environmental experience.
Compliance with Green Standards: Helps projects achieve certifications like LEED and BREEAM.
III. Analysis of Product Segments & Application Scenarios
Features: Dustproof, waterproof, corrosion-resistant (potentially explosion-proof), built for harsh environments.
Applications: Food processing plants, cold storage, parking garages, underground passages, car washes.
Dimming Need: Adjusts light levels based on varying foot or vehicle traffic at different times for energy savings.
Features: High efficacy, long lifespan, precise light distribution, integrated smart control interfaces.
Applications: City main roads, residential streets, parks, highways.
Dimming Need: Automatically reduces power output late at night (e.g., alternating lights or uniform dimming), acting as nodes in smart city IoT networks.
Features: High brightness, glare control, suitable for installation in tall spaces.
Applications: Logistics warehouses, manufacturing workshops, aircraft hangars, sports arenas.
Dimming Need: Enables zone control, integration with daylight harvesting sensors, and adaptation to different operational modes (e.g., cleaning mode, production mode).
IV. Why Choose the ODM Model? Value Beyond Simple Procurement
What is ODM? The ODM provider offers a complete solution from design, R&D to manufacturing.
Advantages of an ODM Manufacturer:
Customization Capability: Deep customization based on specific project needs (size, wattage, CCT, dimming protocol, aesthetics).
Technical Integration Strength: Strong ODMs expertly integrate dimming drivers, smart modules, and luminaire structure, ensuring system stability.
Cost-Effectiveness: Economies of scale and vertical integration lead to more competitive pricing.
One-Stop Service: Provides technical support, certification assistance (UL, DLC, CE, RoHS), logistics, and after-sales service, simplifying the process for you.
Focus on Core Business: Allows buyers to concentrate on their own brand building and market sales.
V. How to Identify a High-Quality Dimmable LED Lighting ODM Partner
Technical R&D Capability: Does they have an independent R&D team? Can they offer multiple dimming solutions?
Product Quality & Certifications: Are international certifications in place? What warranty terms are offered?
Production & Testing Equipment: Are automated production lines used? How is product consistency and reliability ensured?
Project Cases & Experience: Are there successful cases in similar fields? Can they provide references?
Communication & Service: Are they responsive? Do they strive to understand your needs and offer professional advice?
VI. Future Outlook
IoT Integration: Luminaires will become data collection points within the Internet of Things.
Li-Fi (Light Fidelity): Utilizing light for wireless data transmission.
Advanced Human-Centric Lighting: Automatically adjusting light spectrum and intensity based on human circadian rhythms.
Predictive Maintenance: Using system data to pre-emptively warn of potential luminaire failures.